DC radiator fans play an essential role in cooling systems across various industries, especially in automotive and electronic applications. These fans help maintain operating temperatures by circulating air through radiators, preventing overheating and ensuring efficient performance. Given their importance, DC radiator fans are manufactured in different types,each with specific features designed to meet particular requirements.
One of the primary ways to classify DC radiator fans is based on their power supply characteristics. As the name suggests, DC radiator fans operate on direct current (DC) power, typically sourced from batteries or DC power supplies. Common voltage ratings include 12V, 24V, and 48V, with 12V being standard in automotive applications. The voltage rating affects the fan's speed, power consumption, and torque. Selecting the correct voltage ensures compatibility with the system and efficient performance.
Another major classification criterion is the fan blade design. The shape, size, and number of blades significantly influence airflow and noise levels. Some DC radiator fans feature curved blades optimized for high airflow at lower noise, while others use straight blades for pressure generation. Blade materials also vary, from plastic composites to metal alloys. Plastic blades are lightweight and corrosion-resistant, suitable for standard applications, whereas metal blades offer higher durability and can handle higher temperatures or harsh environments.
The fan housing type is another important factor in the classification of DC radiator fans. Some fans come with a simple open frame housing that provides basic protection for the blades. Others feature a shroud or ducted housing designed to direct airflow more efficiently through the radiator. Shrouded fans enhance cooling performance by reducing air recirculation and focusing airflow onto the radiator surface. The housing material also varies, typically between metal and plastic, impacting the fan's weight and durability.
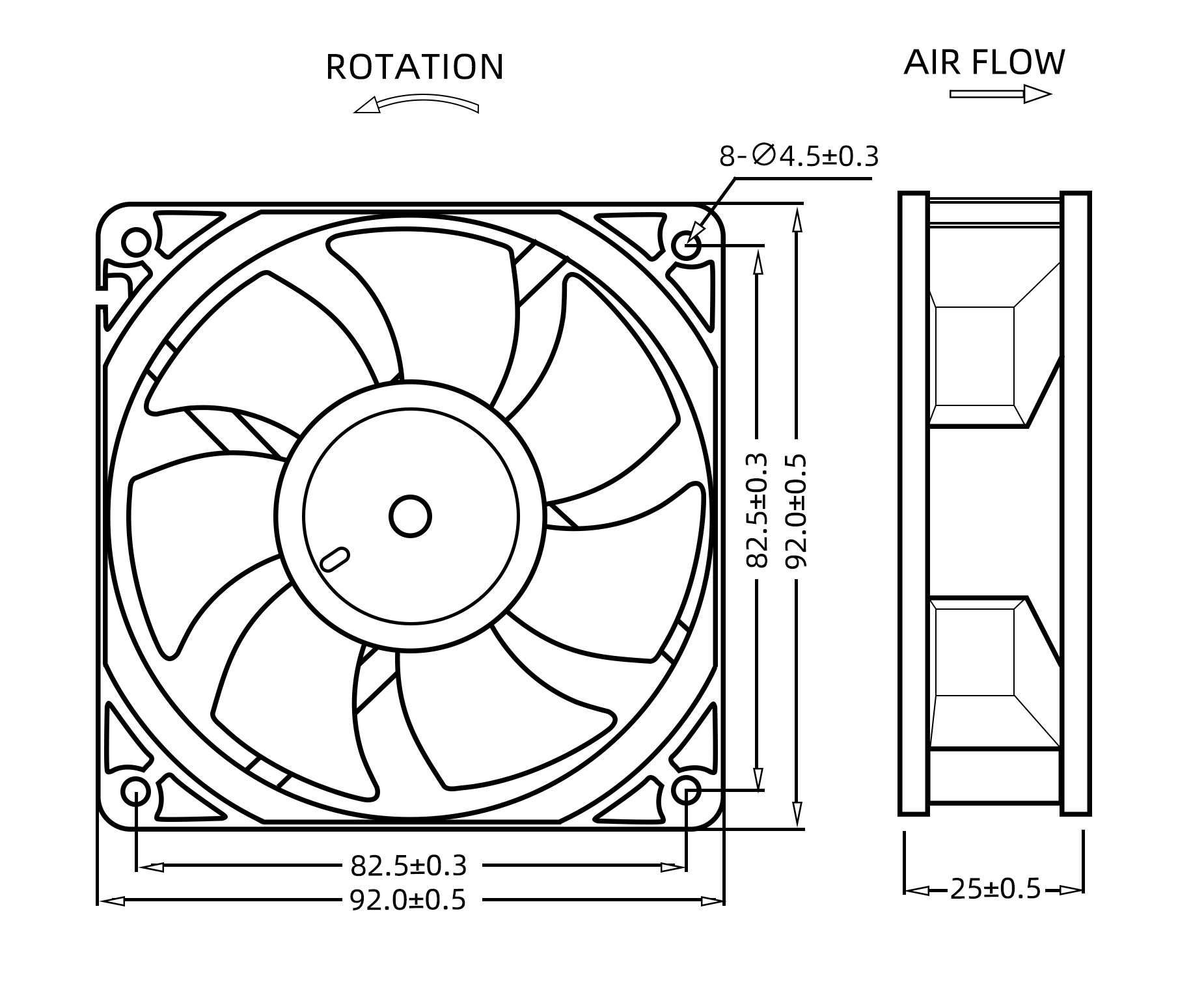
In terms of mounting configuration, DC radiator fans are classified by their installation methods. Axial fans are the common type used for radiator cooling. These fans move air parallel to the shaft, pushing or pulling air directly through the radiator fins. Axial DC radiator fans are favored for their compact size and ease of installation. Alternatively, some systems use blower or centrifugal fans, which move air perpendicular to the shaft and generate higher static pressure. These fans are less common for radiator applications but are used when specific airflow or pressure requirements must be met.
Speed control capability is an essential classification feature of DC radiator fans. Some fans operate at a fixed speed once powered, offering simplicity and reliable cooling. Others incorporate variable speed control, either through pulse width modulation (PWM) or voltage regulation. PWM-controlled DC radiator fans provide precise airflow adjustment based on temperature sensors or control modules, enhancing system efficiency and reducing noise when full fan speed is unnecessary.
The bearing type used in DC radiator fans is another classification factor influencing lifespan and noise level. Common bearing types include sleeve bearings, ball bearings, and fluid dynamic bearings. Sleeve bearings are cost-effective and quieter but may have shorter lifespans under high temperatures or heavy loads. Ball bearings provide longer durability and better performance in demanding environments but can produce more noise. Fluid dynamic bearings offer a balance of low noise and extended life, making them suitable for high-quality DC radiator fans.
Size is a practical classification element for DC radiator fans, with dimensions varying to suit different radiator sizes and cooling requirements. Smaller fans are used in compact systems or electronics, while larger fans are designed for automotive or industrial radiators. Standard sizes include diameters ranging from 80mm to over 200mm. Choosing the right size ensures sufficient airflow without excessive power consumption or noise.

 English
English 中文简体
中文简体 عربى
عربى