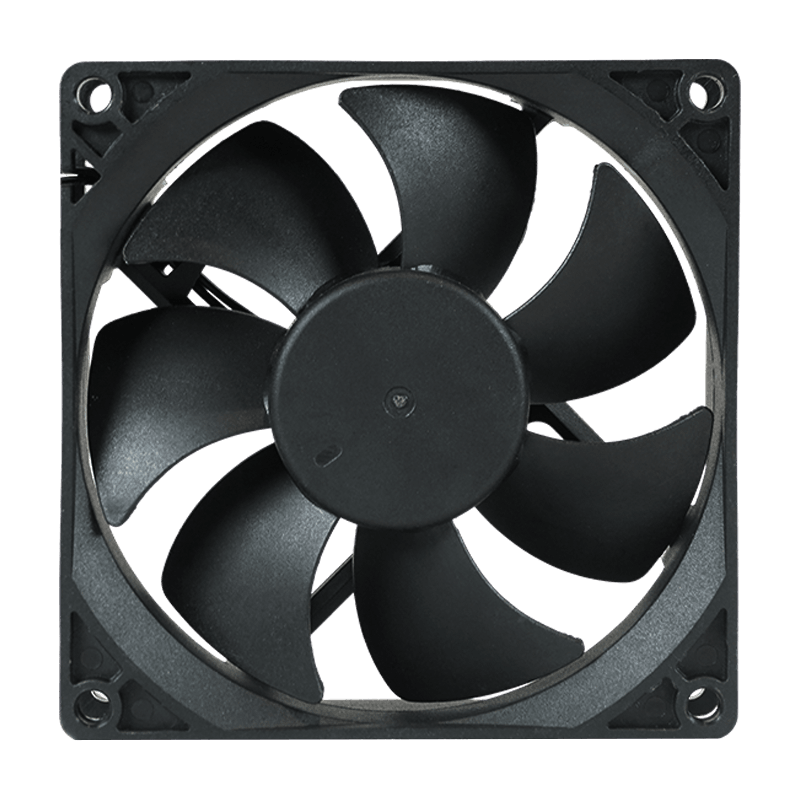
Axial DC Radiator Fans: Direct Airflow Cooling
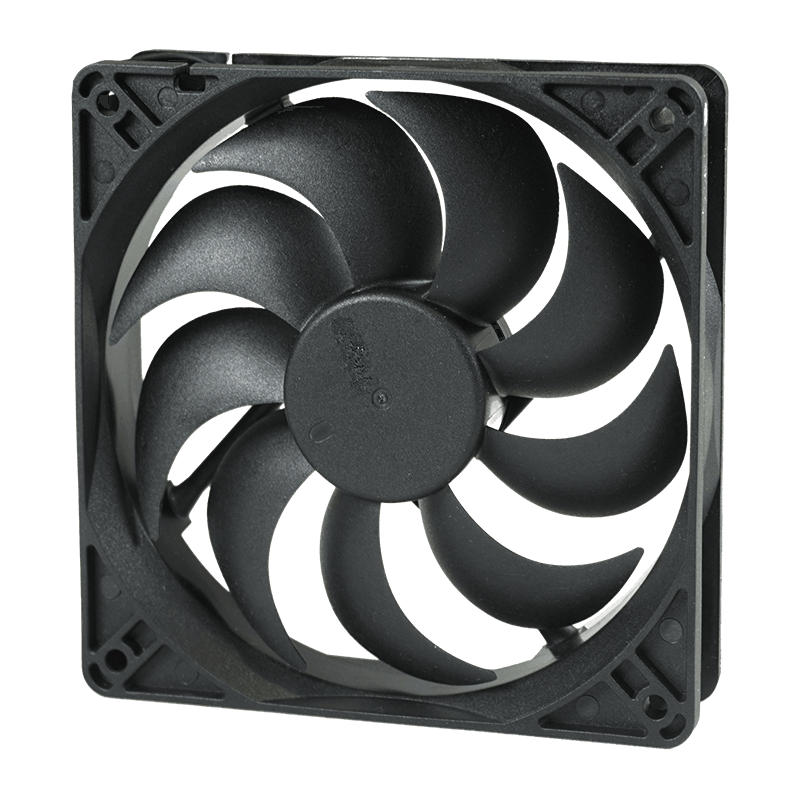
Axial fans are among the most widely used types of DC radiator fans.
Structure: Axial fans consist of a circular frame, blades mounted on a central hub, and a DC motor that drives the blades. The blades are designed to pull air along the axis of rotation, directing airflow through a radiator or heat exchanger.
Function: The fan draws air across the radiator, dissipating heat from the coolant or other fluids. Air passes directly through the fan, providing consistent cooling at varying vehicle speeds or electronic load conditions.
Applications: Axial fans are commonly used in automotive radiators, engine cooling systems, and electronic equipment where airflow needs to be uniform and directed along a specific axis.
Advantages: They provide straightforward installation, predictable airflow patterns, and relatively low manufacturing costs.
Blower DC Radiator Fans: Concentrated Airflow for Specific Areas
Blower fans, also known as centrifugal fans, differ from axial fans in airflow direction and distribution.
Structure: A blower fan features a cylindrical housing with a rotor inside. The blades of the rotor push air perpendicular to the axis of rotation, forcing it through an outlet or duct.
Function: Blower fans generate high-pressure airflow that can be directed through ducts, hoses, or small openings. This type is suitable for cooling specific areas where airflow must be concentrated rather than spread broadly.
Applications: These fans are used in HVAC systems, automotive heater cores, and certain electronic devices where localized cooling is required.
Advantages: Blower fans can deliver higher air pressure compared to axial fans, making them effective for ducted or confined spaces.
Brushless DC Radiator Fans: Efficient and Durable Operation
Brushless DC (BLDC) fans are increasingly used in modern vehicles and electronic cooling systems.
Structure: BLDC fans use a permanent magnet rotor and an electronically controlled stator. They do not have brushes, which reduces mechanical wear and maintenance requirements. These fans may be axial or centrifugal in design.
Function: Electronic controllers regulate the fan speed based on temperature sensors or user settings. Brushless motors provide efficient energy use, quiet operation, and longer service life compared to brushed motors.
Applications: BLDC fans are widely used in modern automotive radiators, power electronics, and computer cooling systems, where precision control and energy efficiency are priorities.
Advantages: They offer adjustable speed, lower noise, and reduced wear, making them suitable for applications requiring consistent performance over extended periods.
Dual-Speed DC Radiator Fans: Adaptive Cooling Performance
Dual-speed DC fans provide two operating modes, allowing them to respond to varying cooling demands.
Structure: These fans use a motor capable of operating at two distinct speeds. The fan blades and frame may resemble standard axial fans, while the motor is designed to switch between high and low speed.
Function: At low engine or device temperatures, the fan runs at low speed to conserve energy and reduce noise. When higher cooling is needed, it switches to high speed, increasing airflow and cooling capacity.
Applications: Dual-speed fans are common in automotive cooling systems where variable airflow is required, including engine radiators, air conditioning condensers, and auxiliary cooling devices.
Advantages: Dual-speed fans offer flexible operation, energy savings, and improved temperature management compared to single-speed fans.

 English
English 中文简体
中文简体 عربى
عربى